What is an L298N?
The L298N is a motor controller that can drive two DC motors, controlling their direction and speed. It operates between 3V and 35V and is widely used in robotics and electronic projects due to its simplicity and low cost.

Price
You can find the L298N motor controller for around €1.40 from international sellers. This makes it a cost-effective option for controlling motors in your Arduino projects.
How Does the L298N Work?
The L298N uses H-bridges to control the motors' direction and speed. By toggling the input pins (IN1/IN2 or IN3/IN4), you can change the current direction to the motor. The speed is controlled using a PWM signal on the enable pins (IEA/IEB).
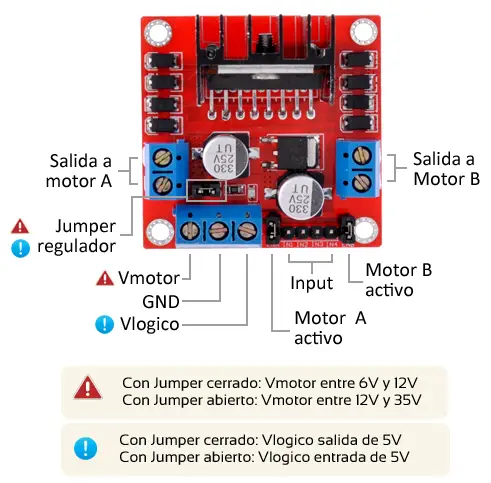
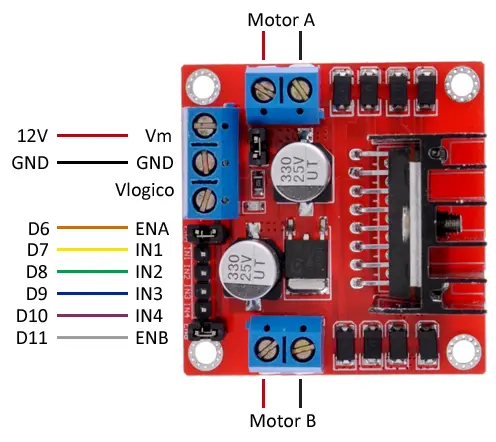
Connection Diagram
The diagram below shows how to connect the L298N to two DC motors and Arduino:
Code Examples
Basic Example: Move Motor A Forward
This example runs motor A forward at 80% speed:
const int pinENA = 6;
const int pinIN1 = 7;
const int pinIN2 = 8;
const int speed = 200; // speed of rotation (80%)
void setup() {
pinMode(pinIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinENA, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(pinIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinIN2, LOW);
analogWrite(pinENA, speed);
delay(1000);
}
Advanced Example: Full Motor Control
This example controls two motors, toggling between forward, backward, and stop states:
const int pinENA = 6;
const int pinIN1 = 7;
const int pinIN2 = 8;
const int pinENB = 11;
const int pinIN3 = 9;
const int pinIN4 = 10;
const int speed = 200;
const int waitTime = 2000;
void setup() {
pinMode(pinIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinIN3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinIN4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinENB, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
moveForward(pinENA, pinIN1, pinIN2, speed);
moveForward(pinENB, pinIN3, pinIN4, speed);
delay(waitTime);
moveBackward(pinENA, pinIN1, pinIN2, speed);
moveBackward(pinENB, pinIN3, pinIN4, speed);
delay(waitTime);
stopMotor(pinENA, pinIN1, pinIN2);
stopMotor(pinENB, pinIN3, pinIN4);
delay(waitTime);
}
void moveForward(int enablePin, int in1, int in2, int speed) {
digitalWrite(in1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
analogWrite(enablePin, speed);
}
void moveBackward(int enablePin, int in1, int in2, int speed) {
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, HIGH);
analogWrite(enablePin, speed);
}
void stopMotor(int enablePin, int in1, int in2) {
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
analogWrite(enablePin, 0);
}