Electromagnets
Electromagnets attract ferromagnetic objects using a magnetic field generated by a current-carrying coil.

Applications include cranes, robotic arms, and fixation devices for robots on metal surfaces.
Magnetic Actuators
These actuators operate like electromagnets but include a mobile magnetic core for linear motion.

They are fast but have limited travel distances and forces.
Linear Actuators
Linear actuators combine a DC motor with a worm screw for precise linear motion.

Common applications include awnings, lifts, and automated doors.
Worm Screw and Sliding Actuators
Similar to linear actuators but with an intermediate sliding element for precise movement.

They are commonly used in CNC machines and 3D printers.
Linear Motors
Linear motors provide high-speed, high-precision movement using alternating magnetic fields.
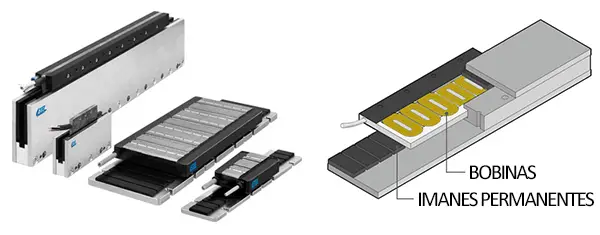
They are costly and primarily used in industrial applications and advanced systems like railguns.
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Actuators
Hydraulic systems provide high precision and force, while pneumatic systems are faster but less precise.

These systems are typically used in industrial and heavy machinery applications.
Summary Table
| Actuator | Speed | Force/Torque |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnet | - | High |
| Magnetic Actuator | High | Medium |
| Linear Actuator | Low | High |
| Worm Screw Actuator | Low | High |
| Linear Motor | Very High | Very High |
| Hydraulic/Pneumatic | High | Very High |
Conclusion
Choose the right actuator based on your project's requirements. For high-speed and precision tasks, linear motors are ideal but expensive. Hydraulic and pneumatic actuators are best for heavy-duty applications, while simpler tasks may be served by electromagnets or linear actuators.