What is a Servo?
A servo is a motor capable of precise angular control. Commonly used in robotics, servos allow positioning between 0º and 180º.

Servos are available in various sizes, with the SG90, MG90S, and MG996R being the most popular for hobby projects due to their cost-effectiveness.
Price
- SG90: Torque: 1.4 kg·cm, Price: €1.20
- MG90S: Torque: 1.8 kg·cm, Price: €2.00
- MG996R: Torque: 13-15 kg·cm, Price: €3.70
These servos are perfect for various projects, including robotic arms, turrets, and more.
How Does a Servo Work?
Internally, a servo uses a DC motor, reduction gears, and a potentiometer to control position based on a pulse width signal.
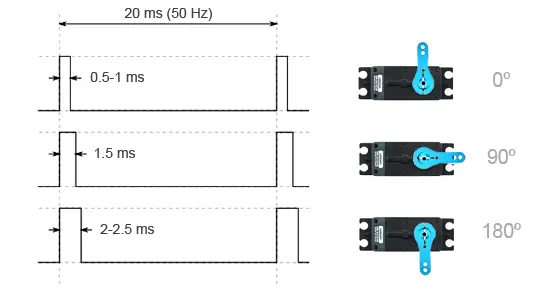
The servo responds to a PWM signal, where pulse widths correspond to specific angles:
- 500-1000 µs: 0º
- 1500 µs: 90º
- 2000-2500 µs: 180º
Assembly Diagram
The servo has three wires:
- Brown/Black: GND
- Red: Vcc (5V-6.5V)
- Orange/White: Signal (PWM)

Connect the signal wire to any Arduino digital pin. For multiple voltage sources, ensure all GNDs are connected.
Code Examples
Sweep Example
The following code makes the servo sweep from 0º to 180º and back:
#include
Servo myservo; // creates the servo object
int pos = 0; // servo position
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo to digital pin 9
}
void loop() {
// Sweep from 0 to 180º
for (pos = 0; pos <= 180; pos += 1)
{
myservo.write(pos);
delay(15);
}
// Sweep from 180 to 0º
for (pos = 180; pos >= 0; pos -= 1)
{
myservo.write(pos);
delay(15);
}
}